“Food for Thought”
Importance of Early Placement of a PEG Feeding Tube
There are many reasons that patients with ALS lose weight – decreased appetite related to shortness of breath, difficulty swallowing, time constraints, anxiety, and depression. However, maintaining body weight is important because excessive weight loss results in muscle loss. During periodic follow-up appointments with your doctor, routine lung function tests will be performed. Your doctor will use specific numbers from these tests to determine your potential need for a PEG feeding tube. Patients are commonly surprised when they receive a PEG tube recommendation, especially if they do not experience difficulty in swallowing. Initially, this may create a similar sense of shock and loss in the patient, much like the initial diagnosis of ALS. Surgery may be initially emotionally distressing and briefly physically challenging, but placement of the PEG tube is necessary and beneficial for long-term nutrition and medicine support.
What happens during placement of PEG tube?
- Small tube (about the diameter of a pencil) is passed through the stomach out to the skin’s surface
- Considered to be a minor surgery
What does a PEG tube do?
- Provides a way of getting food and medication to a patient when swallowing and breathing become difficult
Why Early Placement?
This feeding tube should not be seen like a feeding tube that is placed at the very end of life, as in many other illnesses. Instead, it should be seen as a beneficial form of available treatment that can successfully improve quality of life.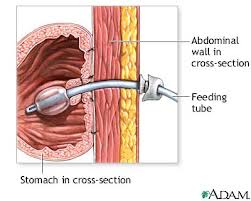
Early placement allows for safe surgery when the diaphragm is in normal position. Late placement may result in more difficulty during surgery. Later on, the stomach may be located abnormally high in the body, due to the weakened diaphragm muscle rising higher into the chest.
In ALS, unlike many other illnesses, a PEG feeding tube may be inserted relatively early in the course of the illness. This can greatly IMPROVE YOUR QUALITY OF LIFE!
Using your PEG tube
When do patients with ALS need a PEG tube?
- When lung function has decreased to a specific level
- When swallowing becomes difficult
- Should be done even before significant weight loss
How often do I need to use my PEG tube for feeding?
- Your dietician/nutritionist will recommend an enteral feeding and advise you on how much and how often
What can be put into my PEG tube?
- Canned or bottled feedings to be determined by your dietician
- If feedings cause upset stomach or diarrhea, let your dietician know because various types of feedings are available
Training
- After surgery, medical staff will train you on how to use and care for your PEG tube
Recommendations
- After each PEG tube feeding, look at the skin around the tube for unusual redness, especially if it’s increasing in size. This may be a sign of infection, requiring treatment by your doctor.
Medicine
Eventually, at very late stage of disease progression, it becomes more difficult to swallow. A PEG tube provides a good route for getting the medication you need.
If you are still able to swallow without difficulty and can breathe comfortably during mealtime without using your ventilator, consider eating normal food orally. Small oral meals consisting of foods that you really enjoy can help increase your quality of life and provide a sense of normalcy. However, be careful! As the disease progresses, difficulty in swallowing may appear gradually and subtlety. Be thoughtful as you chew and minimize speaking when you have food in your mouth.
Meals can consist of both PEG tube feedings and regular food by mouth. As the disease progresses, there will be increased shortness of breath, requiring more PEG tube feedings and less oral feedings.
Both oral and PEG tube feedings may result in increased shortness of breath after the meal. To decrease discomfort, consider setting aside at least 30 minutes after meals to be on the ventilator.
Consult with your physician regarding when food should no longer be eaten by mouth.
Other Benefits to Using a PEG Tube
Keep weight on— As the ability to swallow worsens, there will be weight loss. Whether you are overweight or not, weight loss in a patient with ALS is not good. Severe weight loss, combined with the inability to move, can put a patient at risk for skin breakdown and severe infection. Also, as the diaphragm becomes weaker, accessory muscles around the neck may be used to aid breathing. Increased effort to breathe burns extra calories, which contributes to weight loss, as well.
Time efficiency— Caregiving for a patient with ALS can be time consuming. Tube feeding can either replace or simply supplement meals, whenever you are busy or time is limited.
Choking Hazards
Your physician may prescribe a cough assist machine. This machine will also have the ability to suction food out from your nearby airway. Your respiratory therapist will advise you on how to handle a choking episode.
Drink Up!
Do NOT regularly limit drinking of water to decrease bathroom trips! Not drinking enough water can lead to muscle cramping and constipation.
This is No Time to Diet!
Be careful! Waist size is not a good indictor of weight gain in ALS. Typically, the muscles in the abdominal wall help constrict your waistline and minimize your waist size. However, in ALS, as muscles weaken, they will not be able to remain “tight,” causing your belly to bulge outwards more than normal. Your waist size may increase despite weight loss.
Unless you have a previous medical condition, that requires you to be on a strict diet, such as diabetes, or if you have difficulty swallowing, EAT WHATEVER YOU WISH! You must keep weight on!
TO VIEW THIS INFORMATION IN THE FORM OF A HANDOUT THAT YOU CAN GIVE TO YOUR CAREGIVERS, GO TO THE SITE’S HOME PAGE AND SELECT THE “PRINTABLE CAREGIVER HANDOUTS” TAB!




Overview; Enteral tube feeding; Enteral tube care. Evidence‐based approaches. Percutaneous endoscopically placed gastrostomy tube care; Radiologically inserted …